A 43 year old male comes to JIPMER,Pondicherry, India hospital with acute onset chest pain of two hours duration associated with breathlessness. Patient was a known hypertensive since last two years and was on regular medication. During evaluation in the emergency department patient pulse was 70 beats per minute, Blood pressure was 110/70 mmhg. Patient ECG was done in the emergency department which were shown below.
Click on the image to enlarge it
ECG during acute chest pain
Description of the ECG-Sinus rhythm at 72 beats per minute, normal axis, ST segment elevation in lead II,III,avF, ST segment depression in lead I,avL, V1,V2 suggestive of acute inferior wall myocardial infaction
ECG(Right sided lead)
Description of the ECG-Sinus rhythm at 70 beats per minute, normal axis, ST segment elevation seen in right sided lead suggestive of right ventricular involvement
ECG with posterior lead
Description of the ECG-Sinus rhythm at 67 beats per minute, ST segment elevation seen in posterior lead V7,V8,V9
ECG still showing ST segment elevation
ECG after starting streptokinase thrombolysis at 90 min
ECG still showing ST segment elevation, no evidence of successful thrombolysis
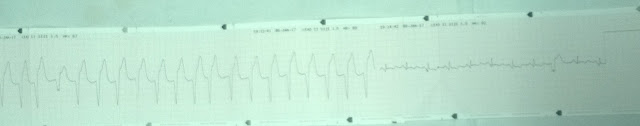
ECG showing accelerated idioventricular rhythm
ECG showing broad complex tachycardia with P wave seen after each QRS complex merged in the QRS segment, heart rate around 100 per minute, QRS duration 120 msec, no capture beat, no fusion beat, no AV dissociation, there is resolution of ST segment in lead II,III, avF
ECG showing accelerated idioventricular rhythm
ECG showing accelerated idioventricular rhythm(Develop after thrombolysis
ECG showing accelerated idioventricular rhythm(Develop after thrombolysis)
ECG showing resolution of ST segment in lead II,III,avF suggestive of successful thrombolysis
Diagnosis Acute inferior wall myocardial infarction with right wall with posterior wall involvement with accelerated idioventricular rhythm with successful streptokinase thrombolysis
Reference- Braunwald 10 th edition, Chapter 52, ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction: Management, page no-1132
Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm
An accelerated idioventricular rhythm typically occurs during the first 2 days, with about equal frequency in anterior and inferior infarctions. Most episodes are of short duration. Accelerated idioventricular rhythm is often observed shortly after successful reperfusion has been established with fibrinolytic therapy. However, the frequent occurrence of this rhythm in patients without reperfusion limits its reliability as a marker of the restoration of patency of the infarctrelated coronary artery and may have different implications following primary PCI. In contrast to rapid VT, accelerated idioventricular rhythm is thought not to affect prognosis, and we do not routinely treat accelerated idioventricular rhythms.
Thank you.










No comments:
Post a Comment